Introduction
Learn how to use Git on Linux with our beginner’s guide, discover the power of Git version control for efficient code management and collaboration.
In the fast-paced world of software development, keeping track of changes, collaborating with team members, and maintaining the integrity of your codebase are crucial aspects. This is where version control systems like Git come into play. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll walk you through the basics of using Git version control on Linux, helping you streamline your development process and collaborate effectively.
Git is a distributed version control system that is widely used in software development. It allows multiple individuals or teams to work collaboratively on a project, tracking changes to source code over time. Git provides a structured and efficient way to manage code revisions, making it easier to coordinate efforts, maintain code quality, and facilitate seamless collaboration in both small and large-scale software projects.
Table of Contents
Key features
Key features of Git include:
- Version Control: Git tracks changes to files and directories over time, creating a history of revisions. This enables developers to revert to earlier versions, review code changes, and collaborate more effectively.
- Distributed System: Each developer has a complete copy of the repository, including its full history. This decentralized approach allows work to continue even without a network connection and enhances collaboration.
- Branching and Merging: Git enables developers to create separate branches of code, allowing for isolated development of features, bug fixes, or experiments. These branches can later be merged back together, preserving the integrity of the codebase.
- Collaboration: Multiple developers can work on the same project simultaneously, and Git makes it possible to integrate their changes seamlessly. This prevents conflicts and ensures that changes are integrated in a controlled manner.
- History Tracking: Git maintains a detailed history of changes made to the codebase, including who made the changes and when. This history can be invaluable for tracking down bugs, reviewing code, and auditing development activities.
- Speed and Efficiency: Git is designed to be fast and efficient, making it suitable for both small and large projects. It uses advanced algorithms to optimize performance and minimize the amount of data transferred.
- Open Source and Widely Adopted: Git was created by Linus Torvalds, the same person behind the Linux operating system, and it is open source. Its popularity has led to widespread adoption in the software development community.
In summary, Git is a powerful tool that provides a structured approach to managing and tracking changes in software projects. It offers benefits in terms of collaboration, version control, and code management, making it an essential part of modern software development workflows.
Setting Up Git
Before diving into the world of version control, you need to ensure that Git is installed on your Linux system. Most Linux distributions come with Git pre-installed, but you can verify its presence by opening a terminal and typing:
git --version
“Git is not just a version control system; it’s a time machine for your code, enabling collaboration and preserving the history of your software’s evolution.”
Installing Git
If Git is not installed, you can install it using your package manager. For example, on Ubuntu or Debian-based systems, you can follow this Step by Step.
Configuring Git
Once it’s is installed, the next step is to configure it with your personal information. Open a terminal and enter the following commands, replacing the placeholders with your own details:
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email "[email protected]"
To commit the changes and create a snapshot of the code at that point, use:
git commit -m "Your commit message here"
Creating a New Git Repository
To start using Git for version control, navigate to your project’s directory in the terminal and run the following commands:
git init
This initializes a new repository in your project folder.
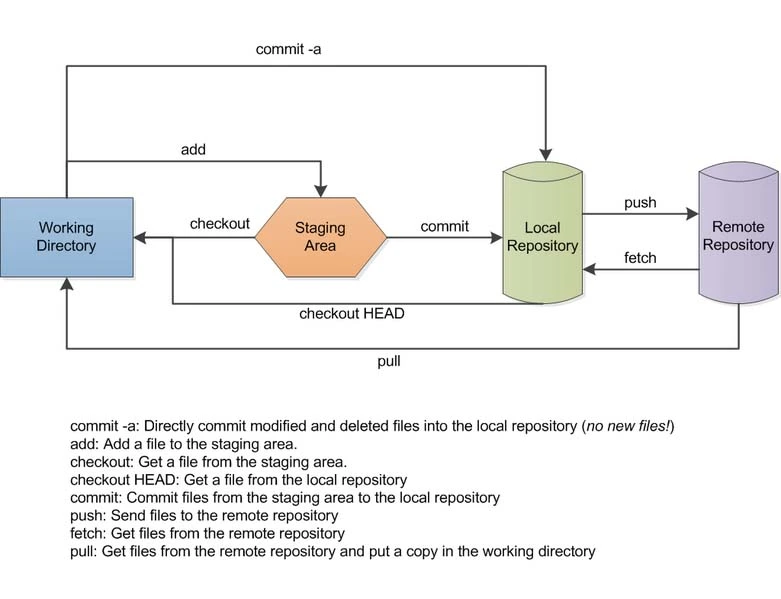
Adding and Committing Changes
As you make changes to your code, Git allows you to track and manage these changes efficiently. To add files to the staging area (where changes are prepared for commit), use the following command:
git add filename
Managing Branches
Branches in Git enable you to work on different features or bug fixes simultaneously without affecting the main codebase. To create a new branch, use:
git branch staging
To switch to the new branch, use:
git checkout staging
Merging Changes
Once you’ve completed work on a branch, you can merge it back into the main branch. For example, to merge the staging branch into the main branch, use:
git checkout main
git merge staging
Remote Repositories and Collaboration
Git allows you to collaborate with others by using remote repositories. To add a remote repository, use:
git remote add origin https://github.com/yourusername/yourrepository.git
To push your local changes to the remote repository, use:
git push origin main
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve taken your first steps into the world of Git version control on Linux. You now have the tools to track changes, collaborate with team members, and manage your codebase effectively. Remember, while this guide covers the basics, Git offers a wide range of advanced features to explore as you continue your journey in software development. Happy coding!
Also Read Our Other Guides :
- How To Install and Config Git on Ubuntu 22.04
- How To Install Jenkins on Ubuntu 22.04
- How To Install and Configure Ansible on Rocky Linux 9
- The 40 Most-Used Linux Commands You Should Know
- How To Install Python 3.11 from Source on Ubuntu 22.04
- How To Create AWS CloudFront: A Step-by-Step Guide
Finally, now you have learned how to use Git Version Control on Linux.